Screening for Breast Cancer
What do you mean by screening and why is it beneficial?
- Screening is a means of finding out the presence of undiagnosed disease in a person without any signs or symptoms. This helps us to identify the disease early. By identifying the disease early in cancer, the patient has a better prognosis, survival rates and might not need some methods of treatment like radiotherapy or chemotherapy. Breast cancer is a very common cancer and when detected early many women are cured of the disease if identified early.
What is the screening regimen for breast cancer recommended?
- Screening regimens for breast cancers are effective if done regularly. Screening regimen recommended for breast cancer is
- Self Breast Examination once every month from the age of 20 years
- Mammogram once every year from the age of 40 years
- Examination by the doctor once every year from the age of 40 years
Why is screening by mammogram usually not done before 40 years of age?
- Screening by a mammogram is usually not done before the age of 40 years because the breasts are usually dense and some early lesions maybe missed by the mammogram.
I have heard women getting breast cancer before the age of 40. How can we prevent it?
- Women can get breast cancers before the age of 40. There is an increasing number of women who get breast cancers before the age of 40 years. Women who are before 40 years need to do self breast examination and consult their doctor if they have any symptoms of breast cancer. Women who have a very high risk as those having the BRCA 1/BRCA 2 gene may have MRI before 40 years every 6 months / year.
How do you do Self Breast Examination?
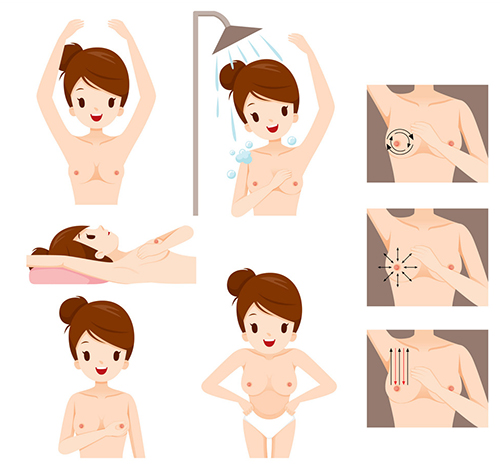
- Self Breast Examination is to be done by all women after they cross the age of 20 years. This is to be done regularly every month. A day in the menstrual cycle is chosen probably 5 to 10 days after periods when the breasts are less tender and painful. It is preferable to keep a constant day eg:- 6th day after the periods get over. One can remind themselves by placing a reminder on their phone or calendar.
- Self-breast examination is started by exposing both breasts in front of a mirror with the shoulders straight and with the arms by the side. One should look for any change in the size and shape of the breast, dimpling, puckering or bulging of the skin, inverted nipple or redness over the breast. The woman then palpates the breast with the pulp of the fingers to feel for any lumps in the breast. Palpation of the breast is to be done systematically, careful not to miss any part of the breast including behind the nipple and over the upper and outer extension of the breast called as the axillary tail. Then both hands are raised up and the breast is looked in the mirror to look out for any asymmetry, changes in the skin and nipple of the breast. The patient then lies down at an angle of 45 degrees placing few pillows underneath the head to recline and then feel the breasts for any lumps. If there is any suspicion of cancer, one needs to see the doctor as soon as possible.
What do you do if you find anything suspicious during Self Breast Examination?
- If you find anything suspicious do not panic. The finding could just be a false positive ( not a cancer in spite of the positive finding). However, it is important that you see a doctor and find out whether it is a false positive finding or an early cancer detection. It is still better to have a few false positive findings than to detect cancers late which could have been found earlier.
Will regular screening with the above regimen detect all breast cancers?
- Mammograms can miss about 5 % of tumours because the breasts are dense or if they are not clear on a mammogram. Mammograms can also produce false-positive results in 5 to 15% of cases and patients may need additional investigations like ultrasound and MRI to prove that they are not cancer. If a tumour starts growing after the mammogram had been done, there is a possibility that the mammogram couldn’t have detected the tumour. Nevertheless regularly following a screening protocol can result in early detection of breast cancers.
When is MRI used as a screening tool?
- MRI breast is used as a screening tool in young patients who have dense breasts, patients who have breast implants which can obscure mammograms and for some patients for whom mammograms are doubtful.
What are the other cancers that can commonly be detected early by screening?
- There are many other cancers that can be found out early by screening such as using Pap Smear for cervical cancer, Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) for prostate cancer, Colonoscopy for colon cancer, UGI scope for oesophagal cancers and CT scan for lung cancers in people who have a very high risk.




