PARATHYROID CANCER
What is a Cancer?
- Cells are the basic building blocks of the tissues and organs of our body. Usually, these cells divide to make new cells in a controlled manner, and beyond a point, the cells are replaced with new cells. This is how our bodies grow, heal and repair. Sometimes, this orderly growth of cells can go wrong due to the mutation or sudden change in the genes which control how cells behave. This can make the cells divide abnormally, producing more abnormal cells, forming a lump called a tumour. These cells cannot stay together, can easily detach from each other and spread via direct contact, lymphatics and bloodstream to different organs in the body.
What are Parathyroid glands?
- Parathyroid glands are 4 small pea-sized glands located adjacent to 4 poles of the thyroid gland in front of the neck. The parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormones, which help regulate the calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood.
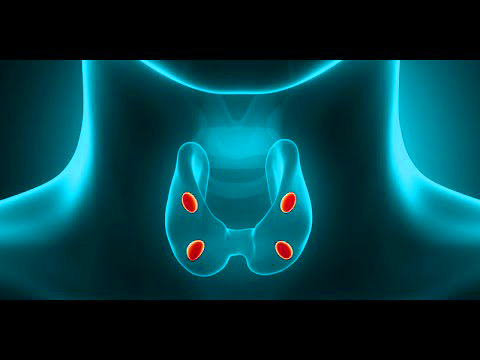
Fig.1 Parathyroid glands seen near the thyroid gland over the neck
How common are parathyroid tumours?
- It is very rare tumor with incidence < 0.5%.
What are the symptoms of parathyroid tumours?
- Swelling in the neck just adjacent to the midline
- Pain in Neck
- Features of high parathyroid hormone levels such as
- Painful bones
- Abdominal pain
- Pain due to stones in the urinary tract (Pain from loin to groin)
- Diffuse muscle ache producing extreme fatigue.
- Psychiatric disturbances.
What are the risk factors of parathyroid Neoplasms?
- The reason why parathyroid neoplasms occur is not known in most people is not known and occur sporadically. They can occur in patients who are exposed to head and neck radiation early in childhood and those who have a strong family history like people with MEN (Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia) syndromes
How does one diagnose Parathyroid Neoplasms?
Parathyroid neoplasms are diagnosed by a detailed history and a thorough clinical examination. The following investigations are also done
- Blood tests Calcium level and Parathyroid hormone levels are high.
- Technetium 99 Sestamibi scan Since there are 4 parathyroid glands in the neck, this test helps identify which parathyroid gland is involved in the disease process.
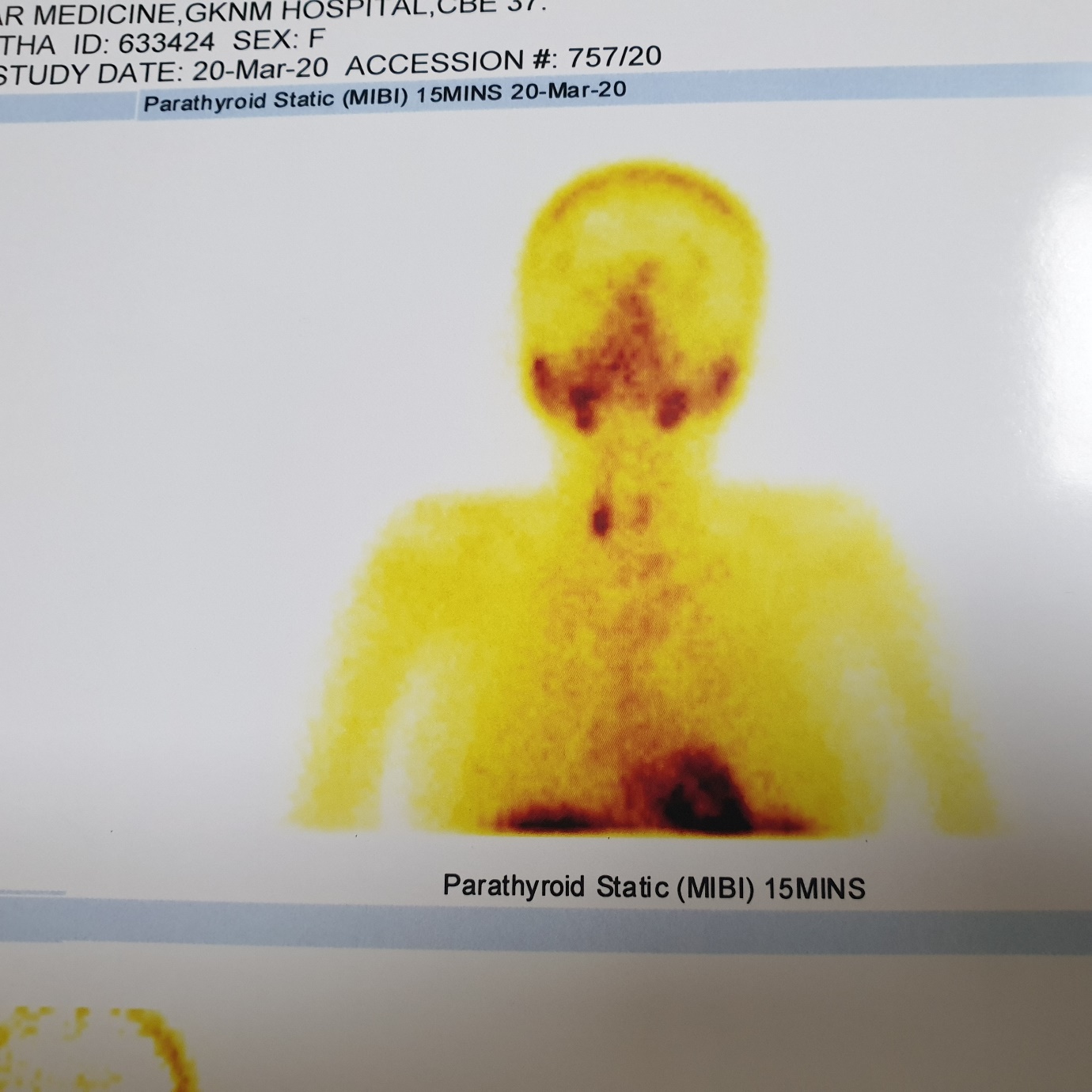
Fig.2 The scan shows the increased uptake in the neck indicative of a parathyroid adenoma
- Ultrasound or Contrast CT of Neck To know the exact anatomical location of the tumour to place the surgical incision appropriately.
- Examination of vocal cords ( Laryngoscopy) To rule out asymptomatic vocal cord palsy.
What are the different types of Parathyroid Neoplasms?
- Parathyroid Adenoma0
Parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumour of one of the parathyroid glands which produce more parathyroid hormones. This is the most common form of parathyroid tumours.
- Parathyroid Hyperplasia
Parathyroid hyperplasia involves the enlargement of all four parathyroid glands. These glands produce excess parathyroid hormones resulting in excess calcium levels in the blood. They are frequently associated with MEN (Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia) Syndromes, a genetic disorder.
- Parathyroid Carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinomas occur as a malignant transformation of a parathyroid adenoma. They are very rare and usually diagnosed after exclusion.
Facts at a glance about surgery and post operative instructions: ( May vary from person to person))
| Type of Anaesthesia | General Anaesthesia |
|---|---|
| Surgery Time | 1 - 2 hours |
| Hospital Stay | 1 - 2 days |
| Mobilisation | 1st day |
| Normal diet | 1st day |
| Suture removal | No suture removal required |
| Self-care | 5 days |
| Full recovery | 2 weeks |
| Return to work | 2 weeks |
What are the treatment options for parathyroid neoplasms?
- Surgery is the most commonly used treatment modality for parathyroid neoplasms. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are used rarely.
What are the advances in parathyroid surgery?
- The parathyroids are seen very close to the thyroid glands and also the nerves responsible for good speech. Hence precise localisation of the tumour is important to avoid damage to the nerves responsible for speech and to avoid injury to the thyroid gland. Intra-operatively we inject Indocyanine green dye to localise the parathyroid glands.-
What are the surgeries done for parathyroid Neoplasm?
Parathyroid Adenoma
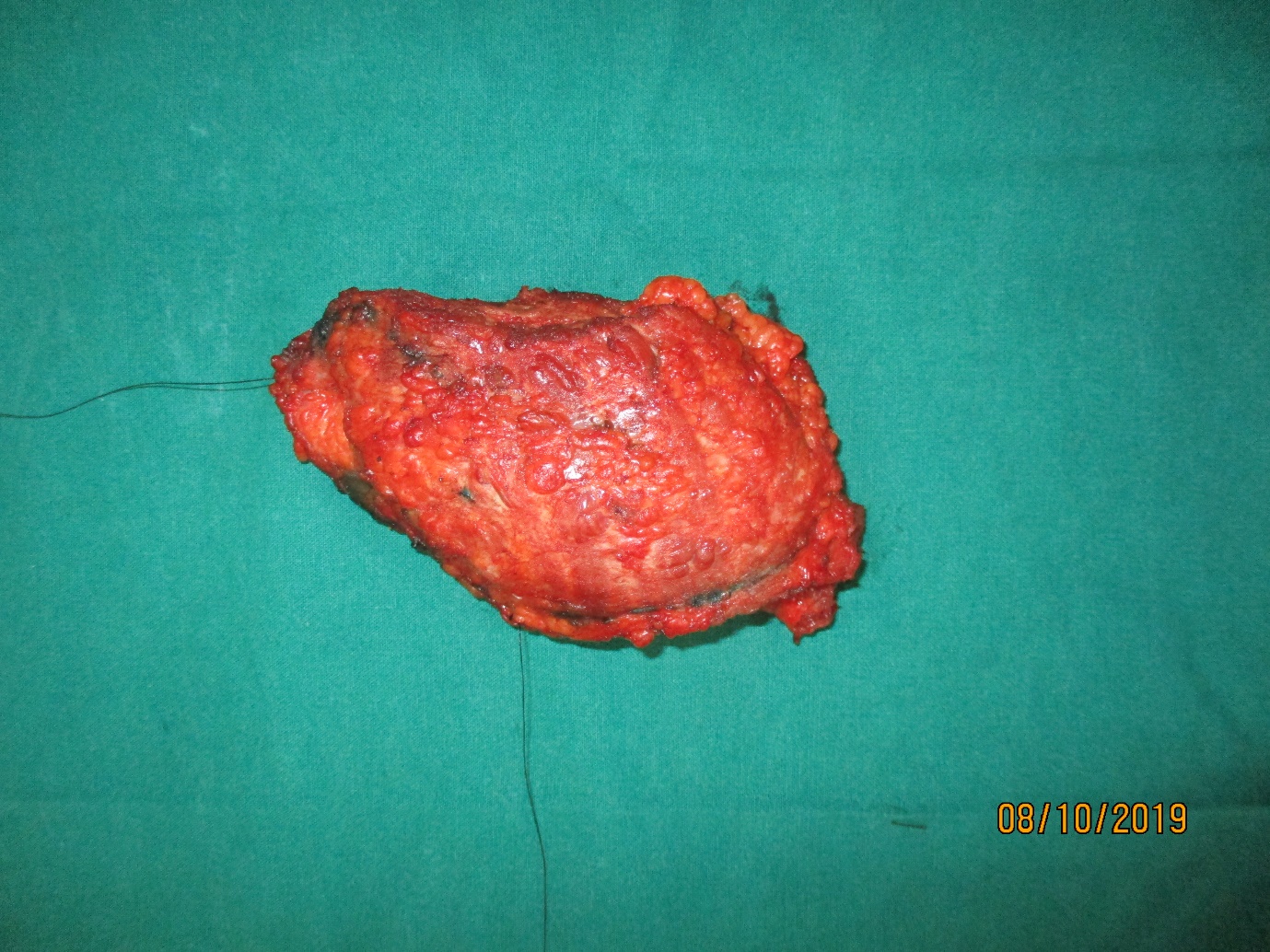
- The involved parathyroid gland is removed. This is called parathyroidectomy.
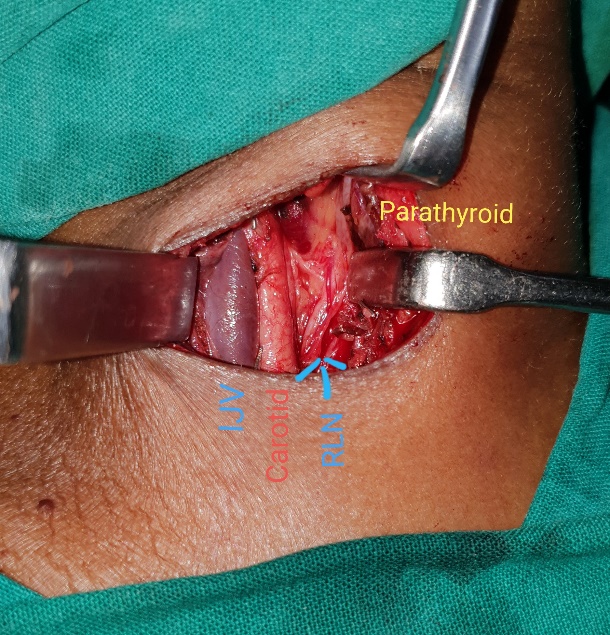
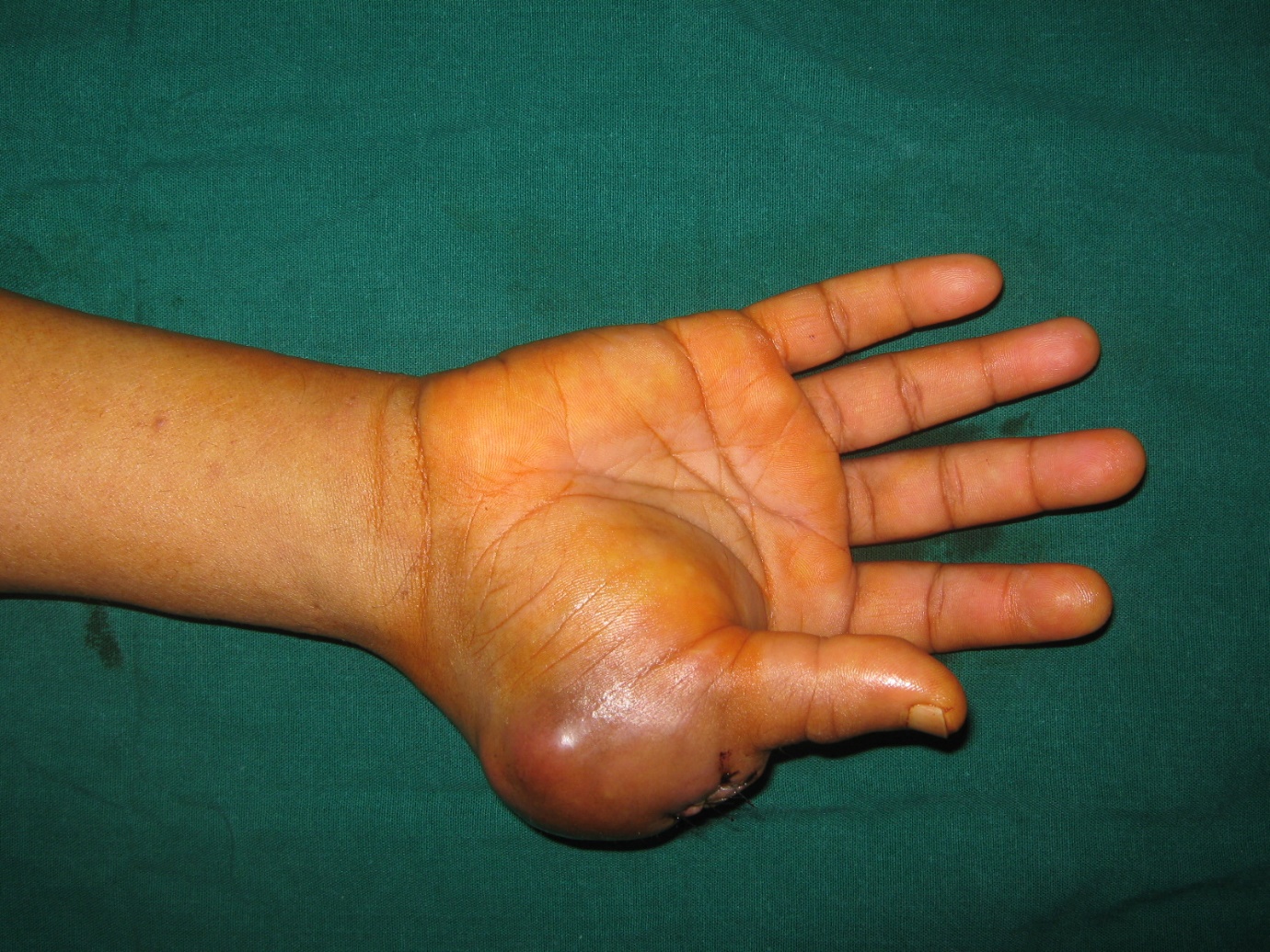
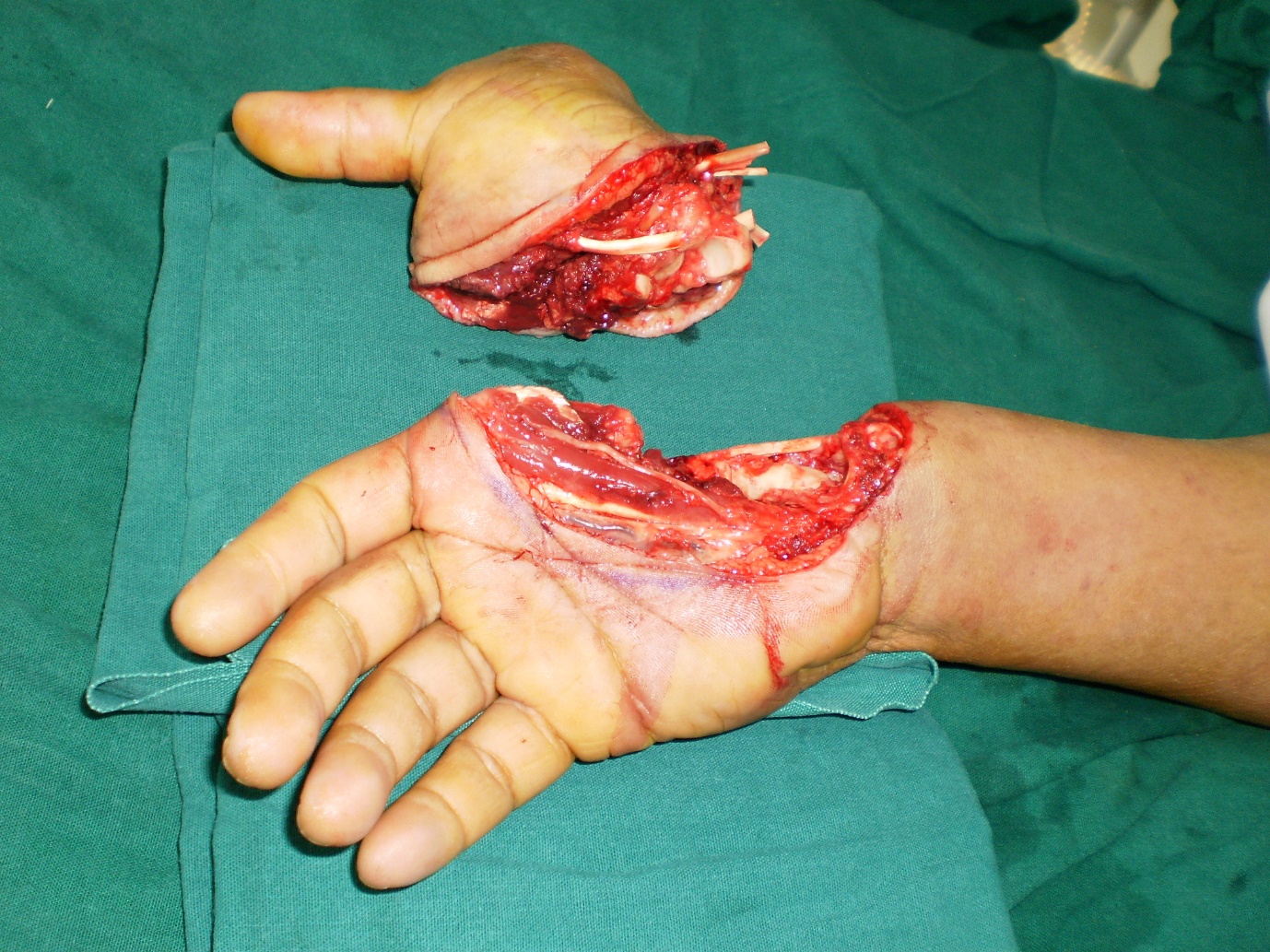
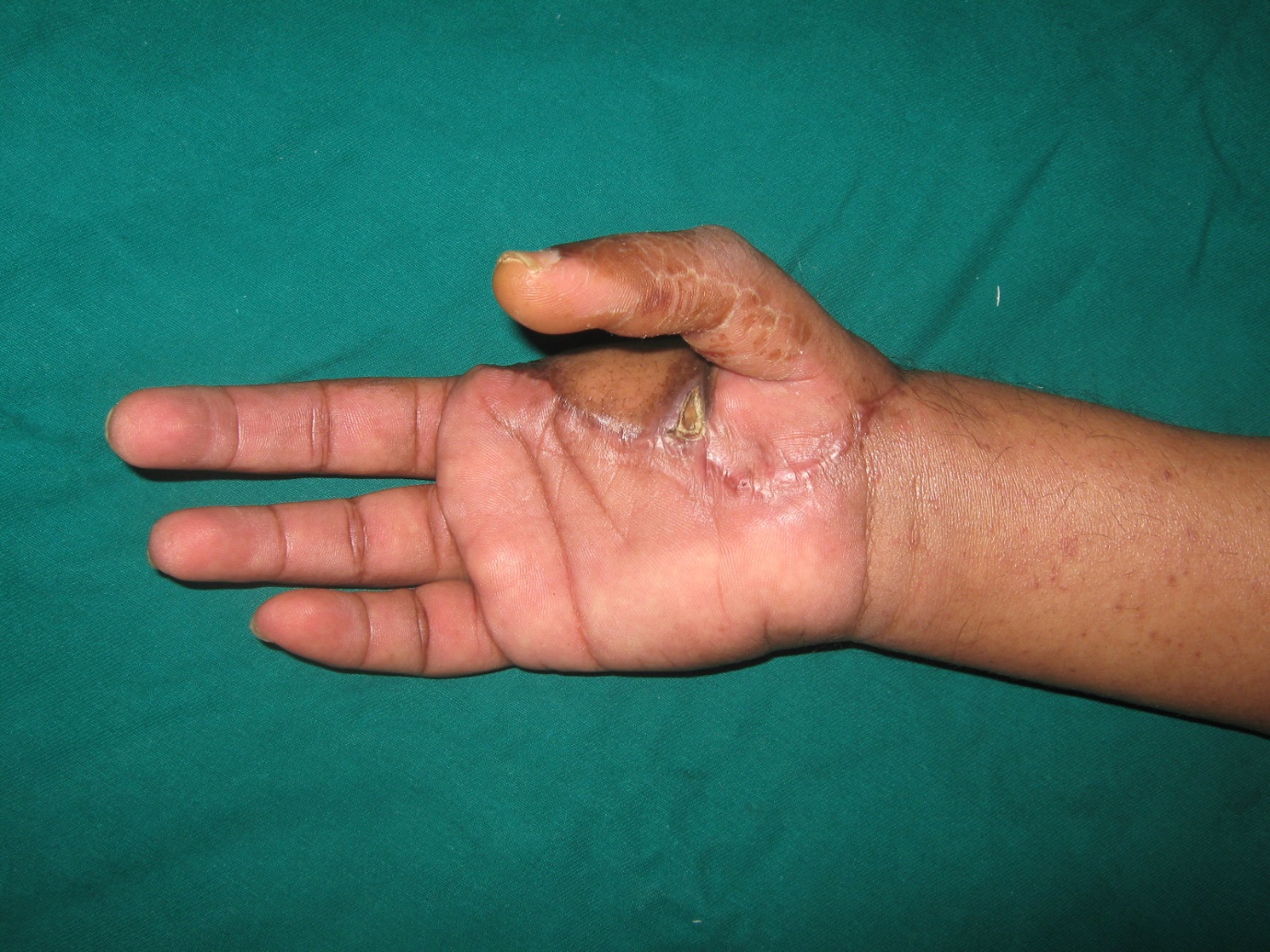
Fig. 3 A. Intra-operative picture of parathyroid adenoma
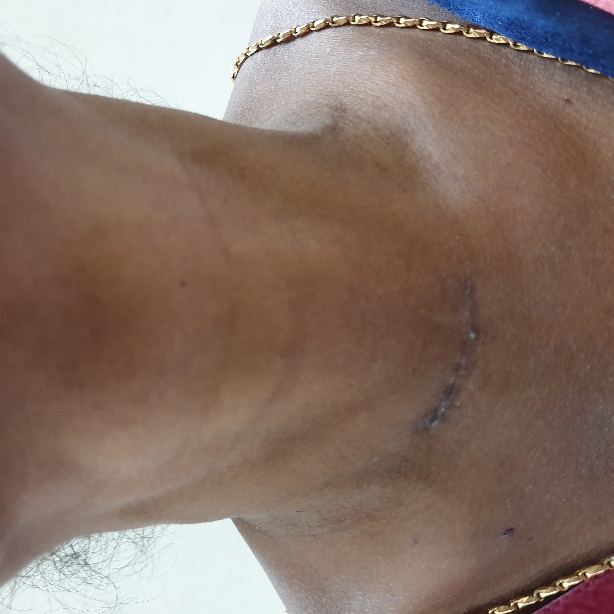
B. Post operative scar
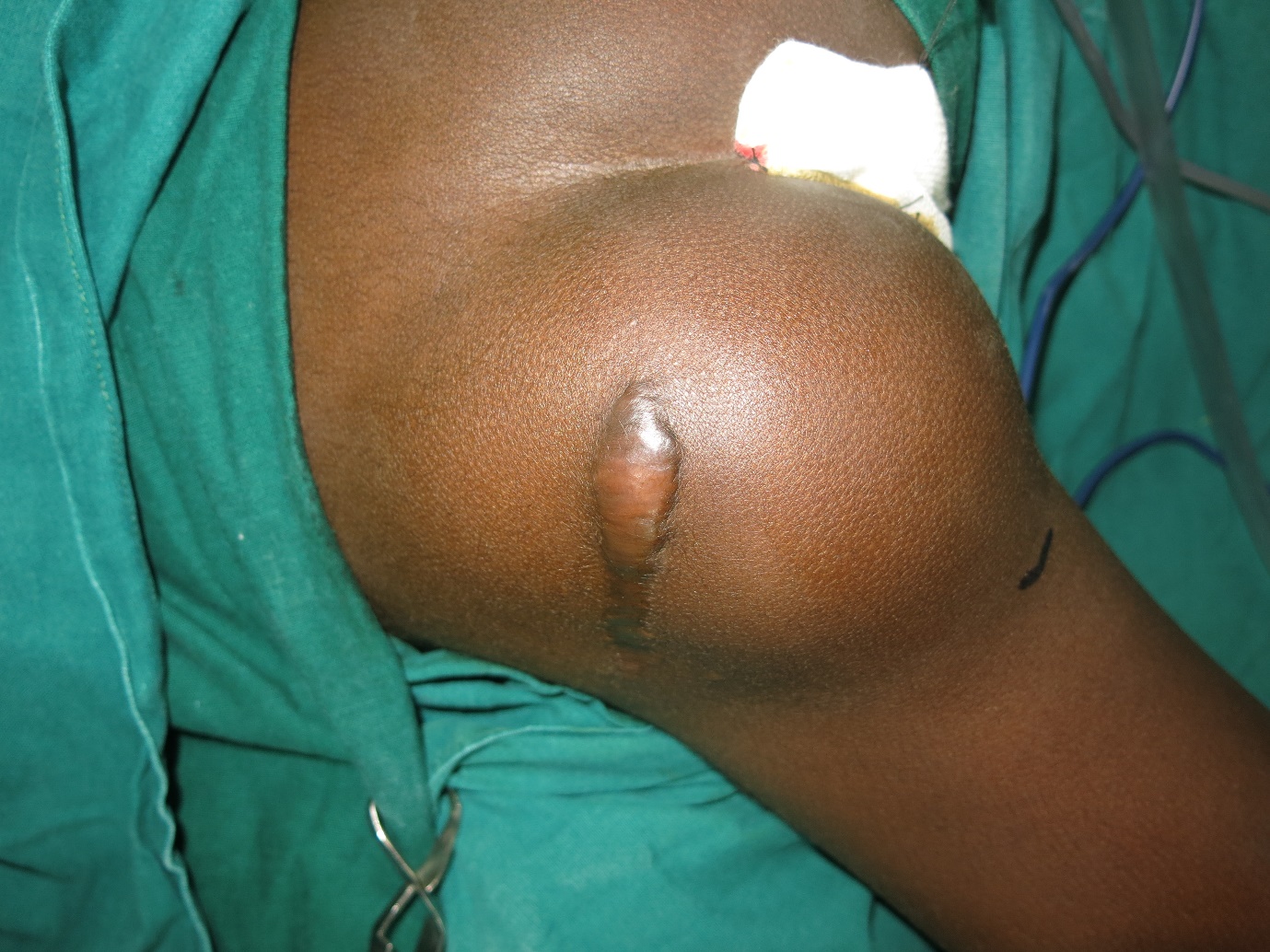
- Parathyroid Hyperplasia
Around three-fourths of the parathyroid glands are removed, minced and implanted in the forearm.
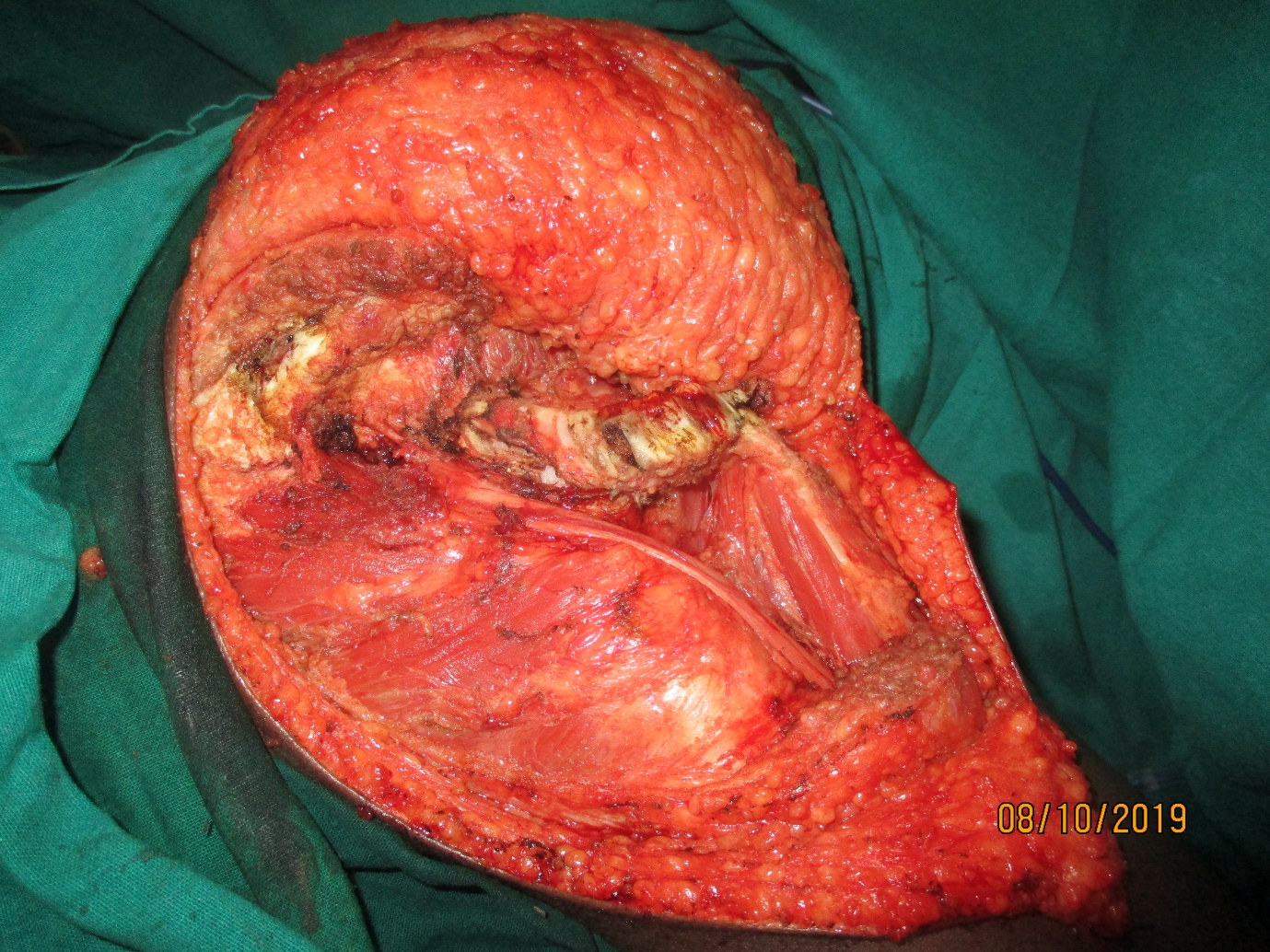
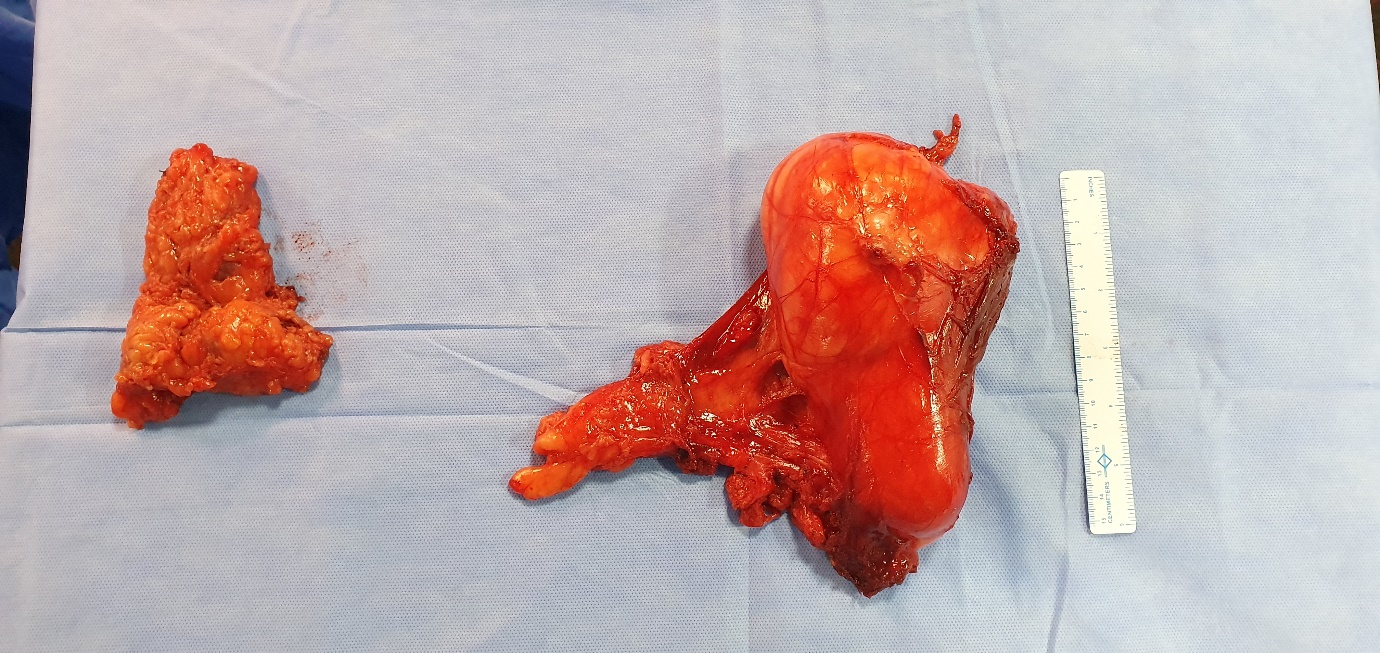
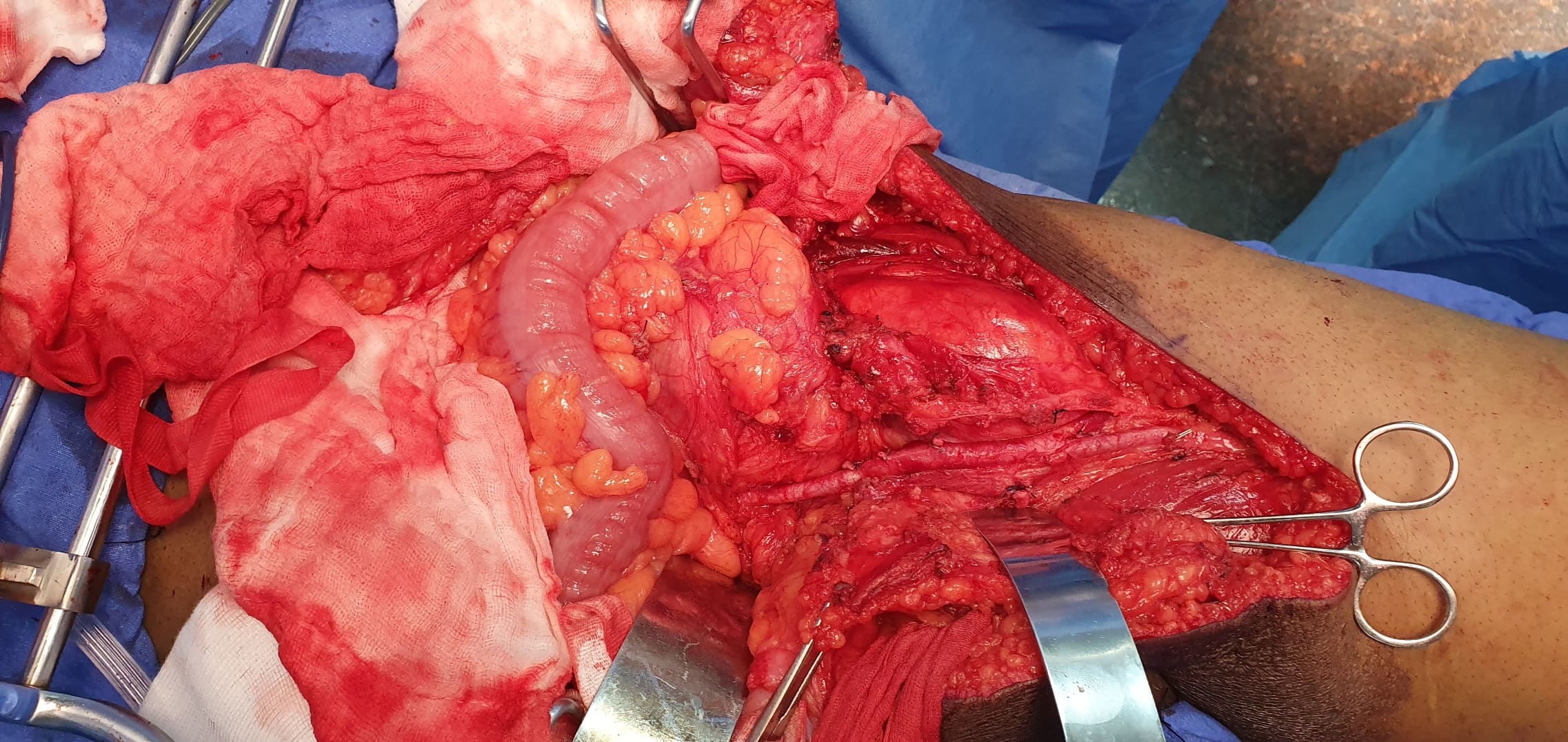
- Parathyroid carcinoma
The parathyroid gland is removed along with adjacent soft tissue.
Facts at a glance about surgery and post operative instructions: ( May vary from person to person)
Chemotherapy is usually included in the treatment protocol if the tumor is chemoresponsive. Whether to be given before or after surgery depends on the hisopathological type of tumor on biopsy specimen.
5 year survival rate for Laryngeal and Pharyngeal Cancers.
| Type of anaesthesia | : General Anaesthesia |
|---|---|
| Surgery time | : 1 - 2 hours |
| Hospital stay | : 1 - 2 days |
| Mobilisation | : 1st day |
| Normal Diet | : 1st day |
| Suture removal | : No suture removal required |
| Self-care | : 5 days |
| Full recovery | : 2 weeks |
| Return to work | : 2 weeks |
What are the Complications expected out of Surgery?
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Seroma
- Lymphoedema
- Deep venous thrombosis
- Small bowel Obstruction( Retroperitoneal)
- Lot of these complications may be reduced by careful planning and meticulous surgical technique.
What is expected in postoperative period?
- Drain tubes will be placed in the surgical bed and will be removed once the volume comes down. After discharge the patient might feel difficulty in walking or using the limb based on the muscle removed during surgery. Hence the patient will be advised to do regular physiotherapy to train the other muscle to improve the outcomes..
What is the chance of cure in Thyroid cancers?
The possibility of survival depends on the cancer stage, site of involvement, grade of the tumour and the patient's compliance with the treatment. The survival of patients with cancer is generally denoted as 5-year survival, wherein the percentage of people surviving at the end of 5years after a cancer diagnosis is noted down. This is given in the tabular column below.
5-year survival rate for Thyroid cancers.
Papillary Follicular Medullary Anasarcoma Limited to thyroid 100% 100% 100% 31% Beyond thyroid or Nodal disease 99% 96% 90% 12% Distant spread 78% 63% 39% 4%
What is TSH suppression therapy?
- TSH ( Thyroid stimulating Hormone) is a hormone produced in the body that helps grow thyroid cancers. This production of TSH can be suppressed by giving higher doses of thyroxine hormones. The TSH level is monitored in frequent intervals, and the dose is adjusted accordingly.
What are the blood test done during Follow up?
TSH ( Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
- TSH is a hormone produced in the body that can facilitate the growth and spread of thyroid cancers. We would like to keep it at a low level. We would like to monitor this level every 3 months for the first 2 years and then periodically lifelong.
- Thyroglobulin & Anti thyroglobulin antibody These are tumour markers that help to identify thyroid cancer recurrence early.




